CFG++ fixes CFG's issues with lower guidance scales,
improving text-to-image quality and invertibility.
T2I Generation Results
(SD v1.5, SDXL)
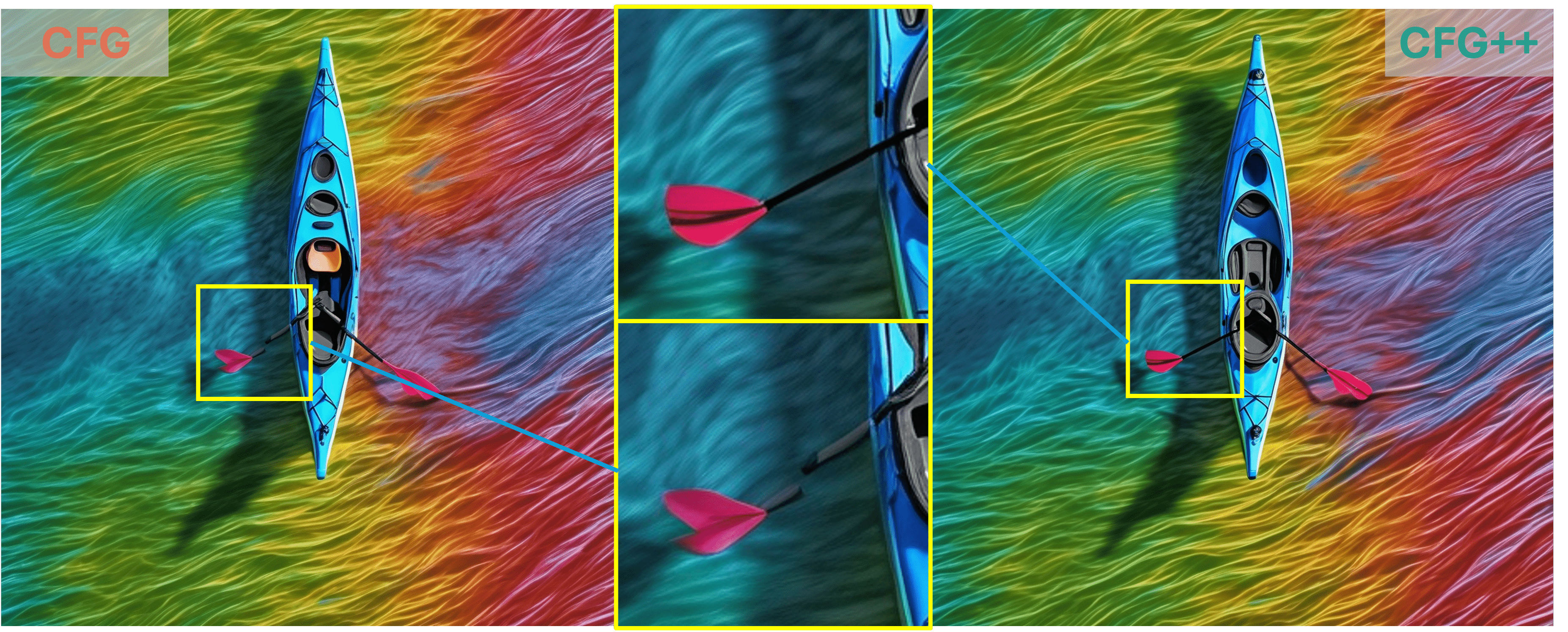
“kayak in the water, optical color, aerial view, rainbow”
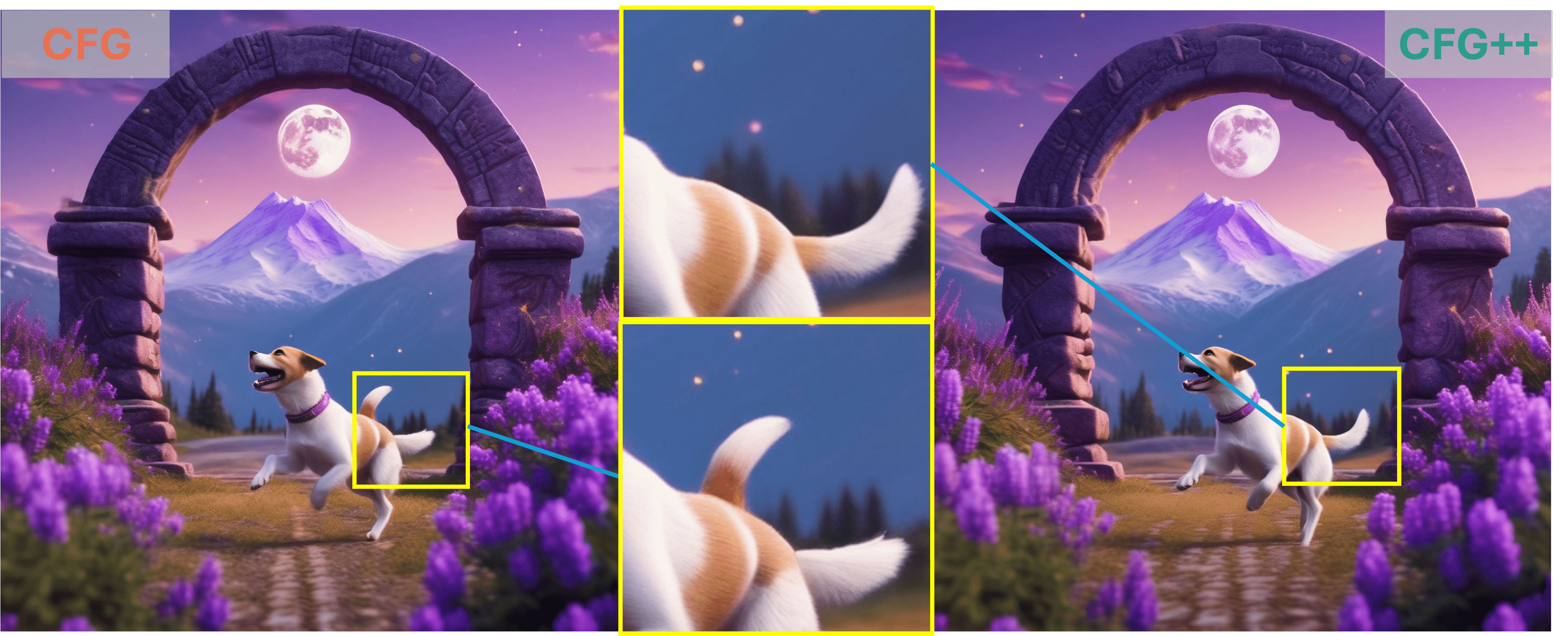

"dog jumping in front of moon gate, purple flowers, snowy mountain"
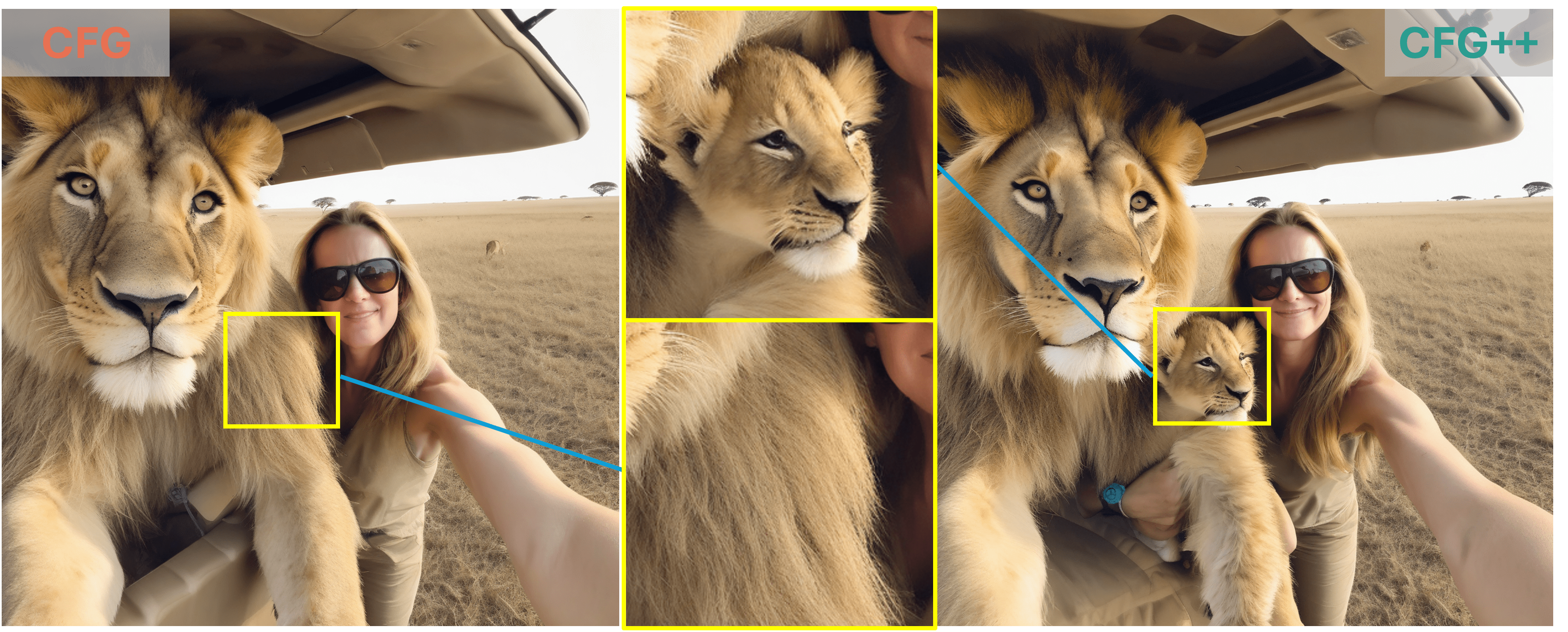
"selfie of a woman and her lion cub on the plains"

"woman sniper, wearing soviet army uniform, in snow ground"
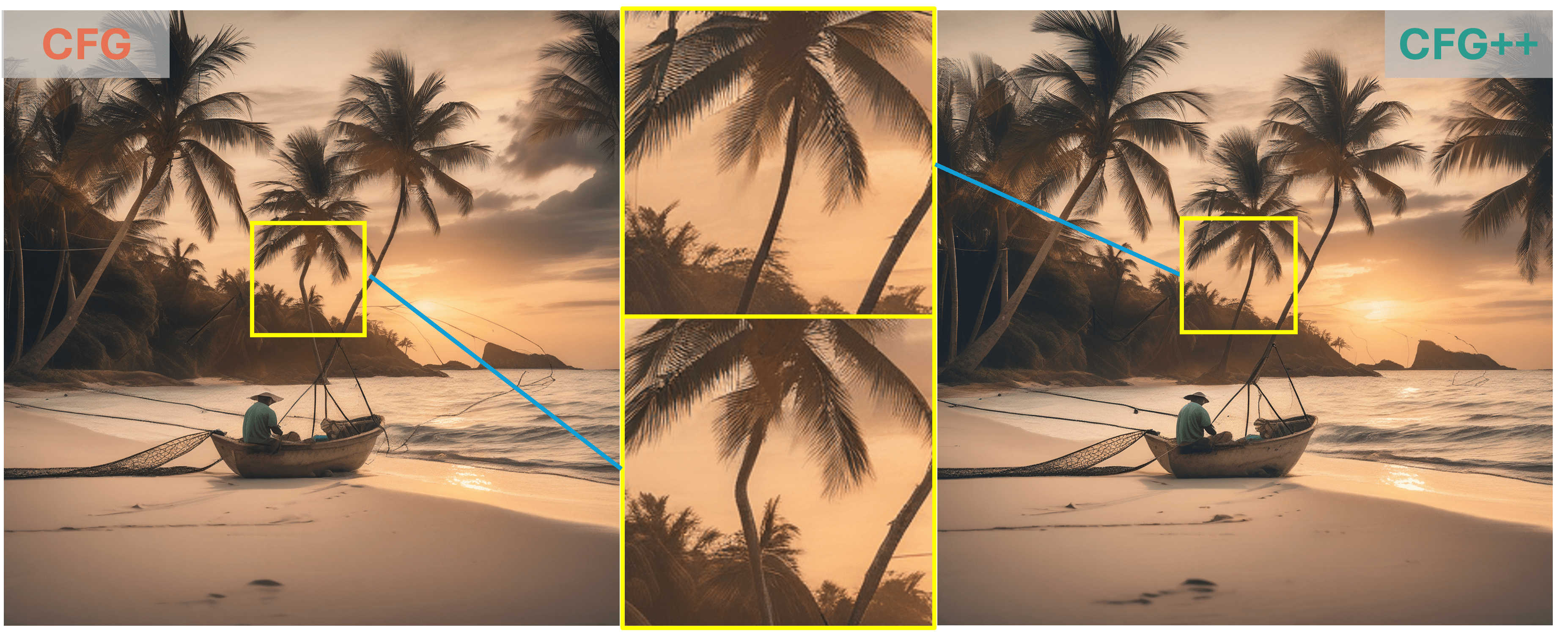

"fisherman sitting on a tropical beach at sunset with bending palm trees"
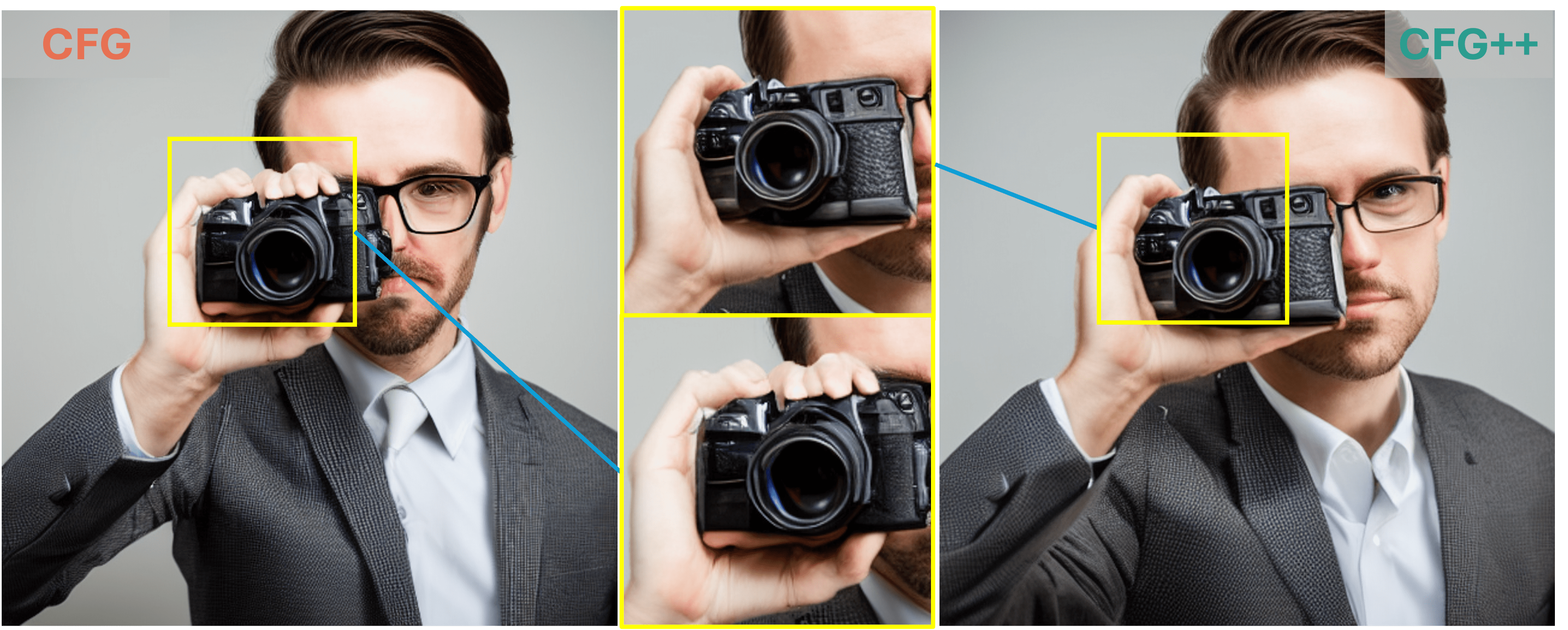
"A man wearing a suit is taking a self portrait with a camera"
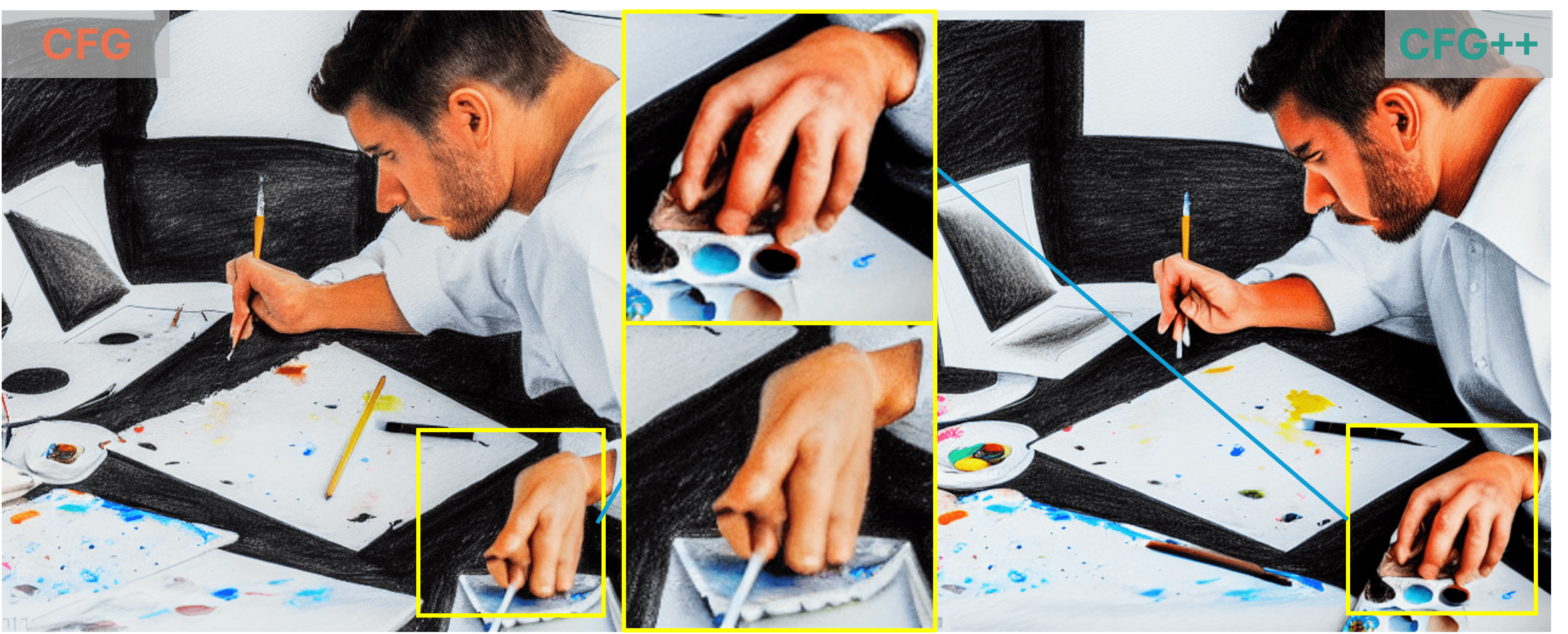

"A painter study hard to learn how to draw …"
Abstract
Classifier-free guidance(CFG) is a fundamental tool in modern diffusion models for text-guided generation.
Although effective, CFG's reliance on high guidance scales presents notable drawbacks.
In response, we introduce simple solution to this seemingly inherent limitation: CFG++ .
This innovation addresses the off-manifold issue inherent in CFG, thereby enabling effective utilization
of small guidance scales (0 < $ \lambda $ < 1) .
| CFG 😓 | CFG++ 😁 | |
| T2I Generation | Mode Collapse and Saturation | Better Sample Quality & Adherence to text |
| DDIM Inversion w/ CFG(++) |
Breakdown | Improves and enables better image editing |
| PF-ODE trajectory | Unnatural, Curved | Smooth, Straighter |
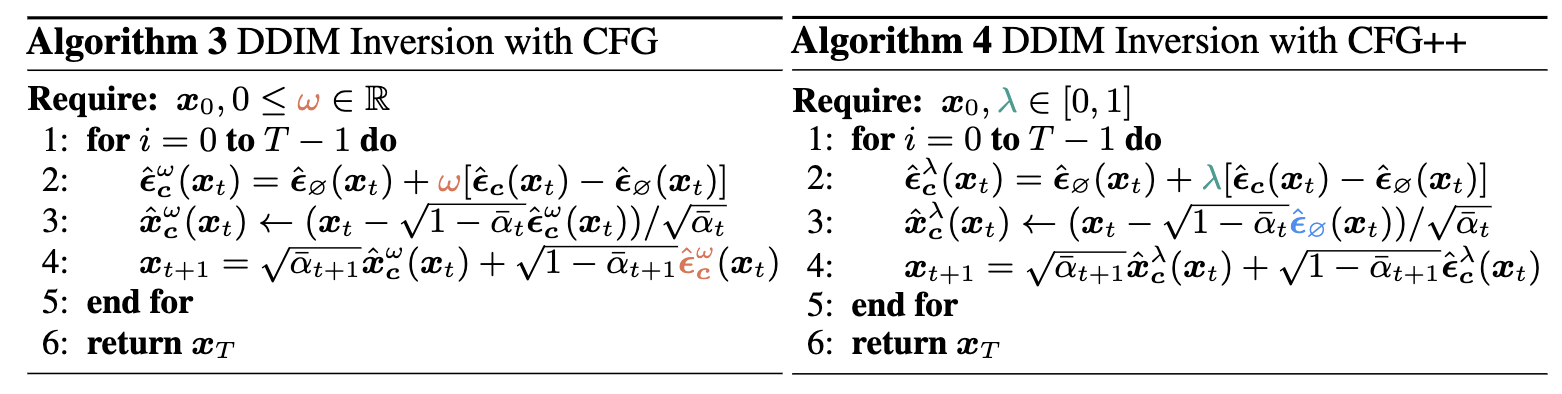
Method
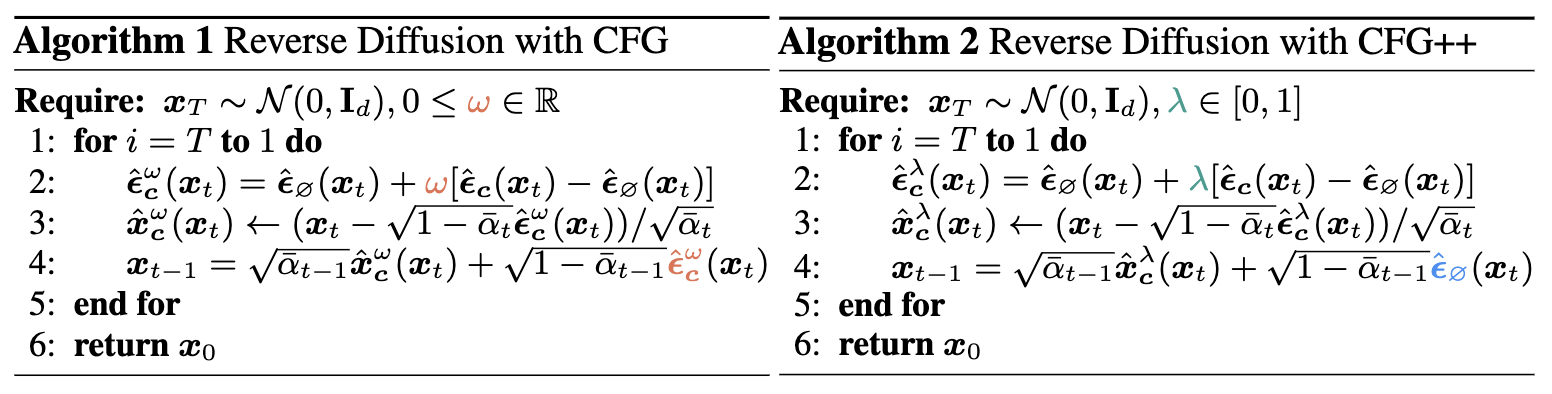
In CFG++, the renoising process after applying Tweedie’s formula should utilize the unconditional noise $ \hat\epsilon_\varnothing $ instead of $ \hat\epsilon^w_c $. This surprisingly simple fix to the original CFG algorithm leads to smoother trajectory of generation. This improvement is also demonstrated in the following visualization of the discrete evolution of the posterior mean.
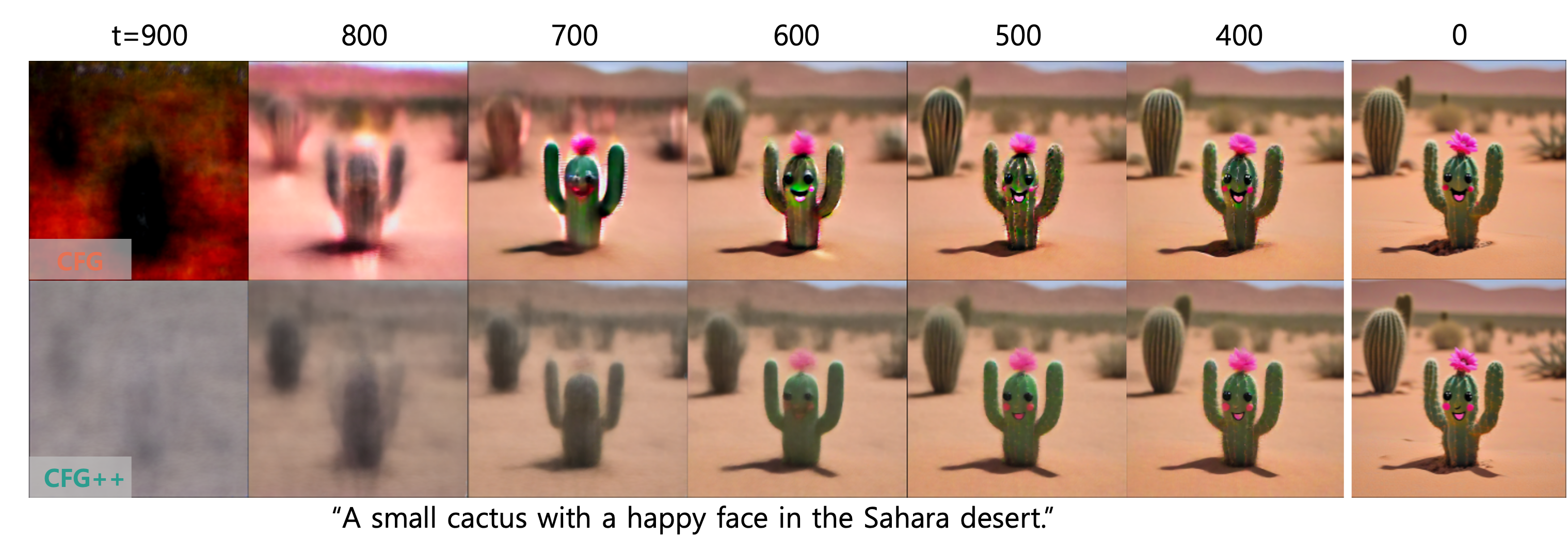

Experimental Results
1. T2I Generation

As demonstrated by the teaser images, our CFG++ method results in a smoother generation trajectory and superior quality. Additionally, we visualize multiple images generated by CFG++ as we increase the guidance scale $ \gamma $. The visualization shows a smooth transition from unconditional sampling towards highly conditional sampling.

We find that the improvement gain from CFG++ is even more dramatic for distilled diffusion models such as SDXL-{turbo, lightning}. We see significant boosts in the quality of the generated images, which is also depicted in the improvements seen in the above figure.
2. Inversion and Editing
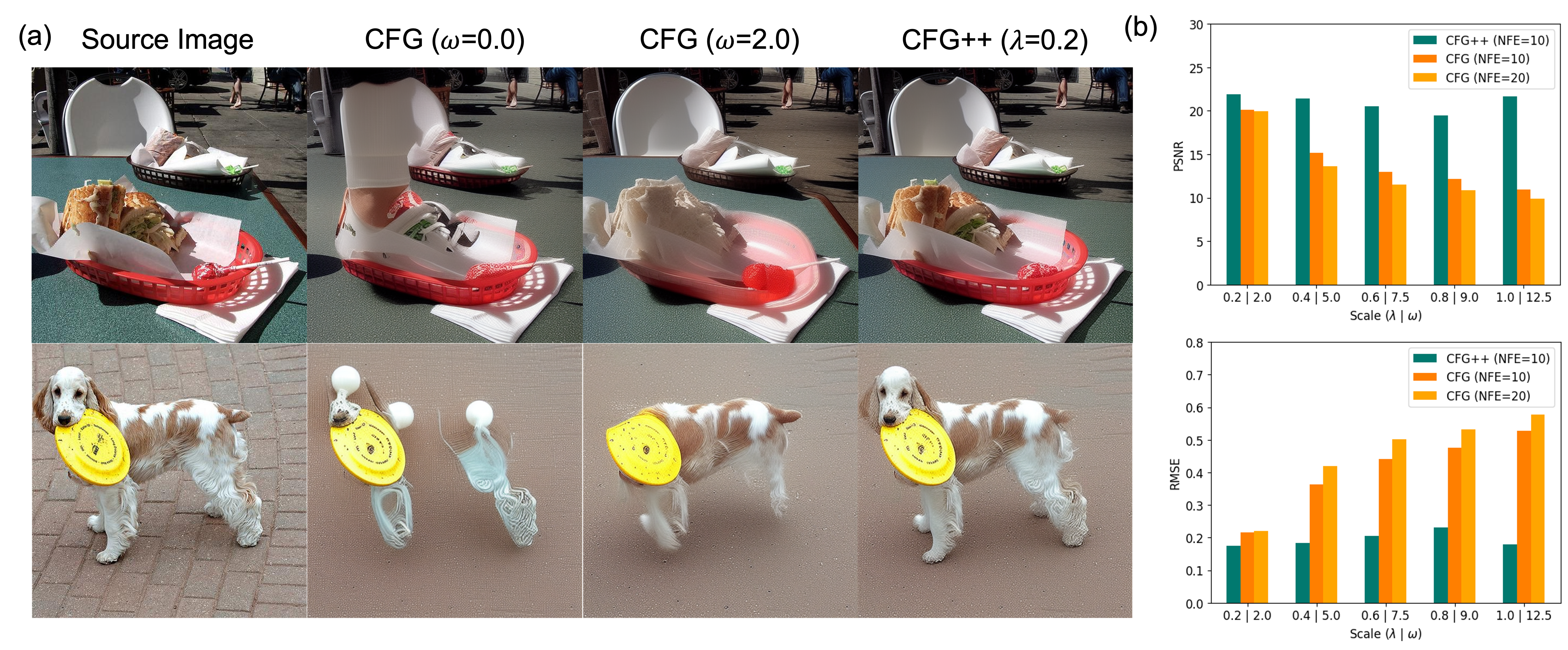
We demonstrate the effect of CFG++ on the image inversion task. (a) Notably, DDIM inversion with CFG++ consistently reconstructs the source image across all guidance scales, whereas DDIM inversion with CFG fails to do so. (b) Quantitative results, including PSNR and RMSE, show a consistent improvement in reconstruction performance.

The figures above compare image editing results using CFG and CFG++ followed by image inversion. During the editing stage, a word in the source text is swapped with the target concept, and this modified text is used as the condition for sampling. Our algorithm successfully works for both synthetic and real images.
3. Text-conditioned Inverse Problems w/ PSLD
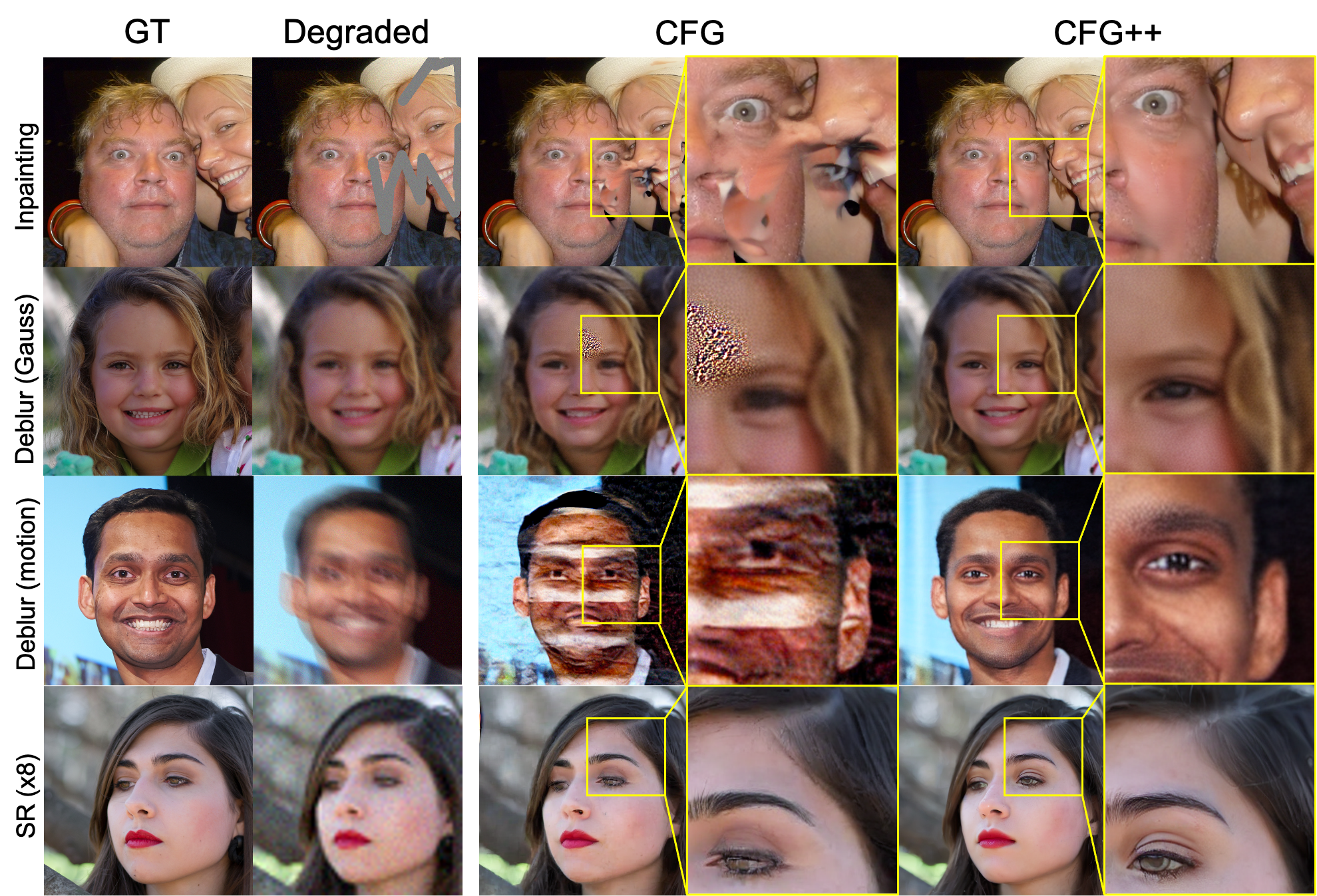

We show that CFG++ enables the incorporation of text prompts into a standard diffusion inverse solvers. Specifically, we focus on comparing the performance of PSLD combined with CFG and CFG++ in solving linear inverse problems. CFG++ consistently delivers high-quality reconstructions across all tasks.